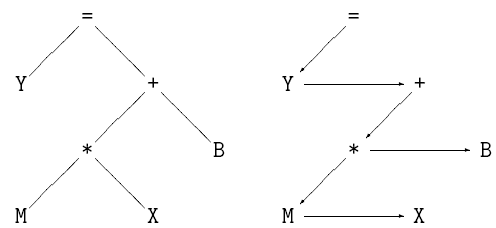
First-Child / Next-Sibling Tree
A node may have a variable number of children. Dedicating many links would be wasteful if the average number of children is much smaller than the maximum, and it would still limit the possible number of children.
Luckily, we can use the same structure as the binary tree, with just two links, and have unlimited children with no wasted space.
y = m * x + b
Tree: Representation:

The layout of nodes in this kind of tree is the same as for a traditional tree; the right-hand links ``fall down'' and become horizontal.
Down arrows represent the first child, while side arrows represent the next sibling.