CS 356: CloudLab Setup
Acknowledgment: This guide has been taken from one written by Daehyoek Kim and Jeongyoon Moon with minor modifications.
You will do your assignments for CS 356 using CloudLab. CloudLab is a research facility that provides bare-metal access and control over a substantial set of computing, storage, and networking resources. If you haven’t worked in CloudLab before, you need to register a CloudLab account. This guide walks you through the CloudLab registration process and shows you how to start an experiment in CloudLab. You should submit a per-group report that shows you have successfully followed the process. Most importantly, it introduces our policies on using CloudLab that will be enforced throughout the semester.
Using Cloudlab is optional if you have access to a Linux machine, for example through your personal computer or a VM and are confident that you can debug any issues. However we recommend you still register for CloudLab since some optional assignments are more fun if you have access to a remote machine.
NOTE: $ [shell_command] indicates to execute [shell_command] in your terminal.
Register a CloudLab Account
- Visit CloudLab and create an account using your UT Austin email address as an email.
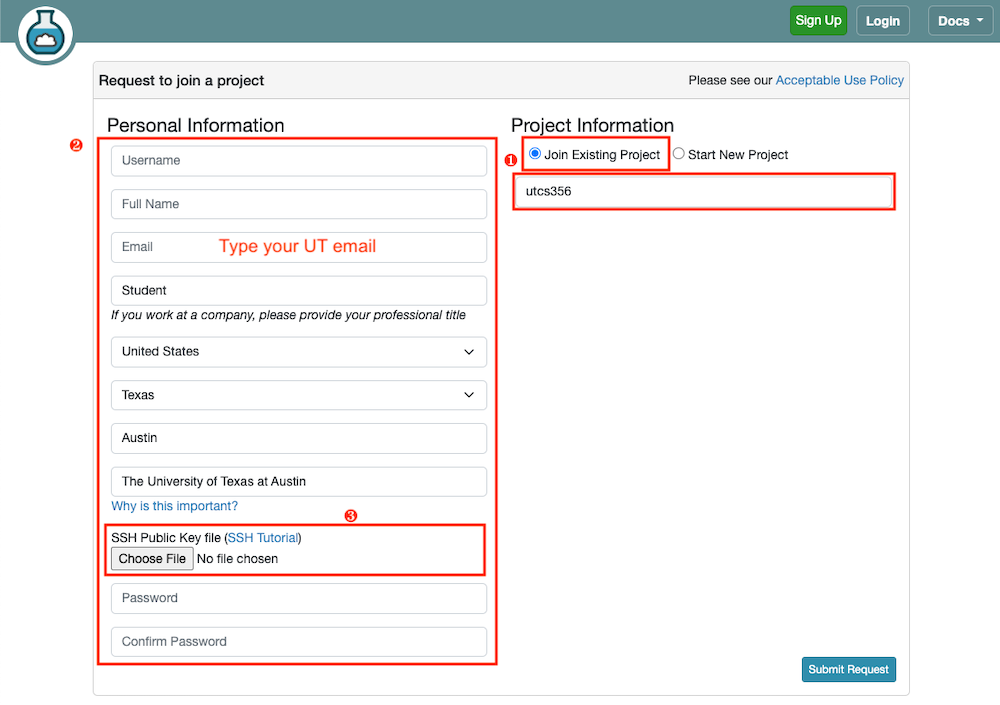
- Select
Join Existing Projectand enterutcs356. - Fill out your information. Use your UT email address as an email.
- Create ssh key pair and upload your public key during the account setup.
- Ubuntu and macOS
- Install OpenSSH
macOS:$ brew install openssh
Ubuntu:$ sudo apt-get install openssh-client openssh-server - Generate a key pair with
ssh-keygen
You can use the below example as it is or try other cryptographic algorithms you prefer (see man ssh-keygen)
Example:$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 - Type enter without typing any character when the prompt asks for the file path and passphrase. The private key will be saved into the default location,
~/.ssh/id_rsa.~/.ssh/id_rsais your private key and~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubis your public key (upload this during the account registration).
+) If you want to save your keys other than the default location, enter a file path (e.g.,~/foo/mykey) to save your private key when the prompt asks for it.~/foo/mykey.pubwould be the public key in this case.
+) If you want additional security, type a passphrase when the prompt asks for it.
- Install OpenSSH
- Windows
- Install MobaXterm and execute it.
- Click
Tools>MobaKeyGen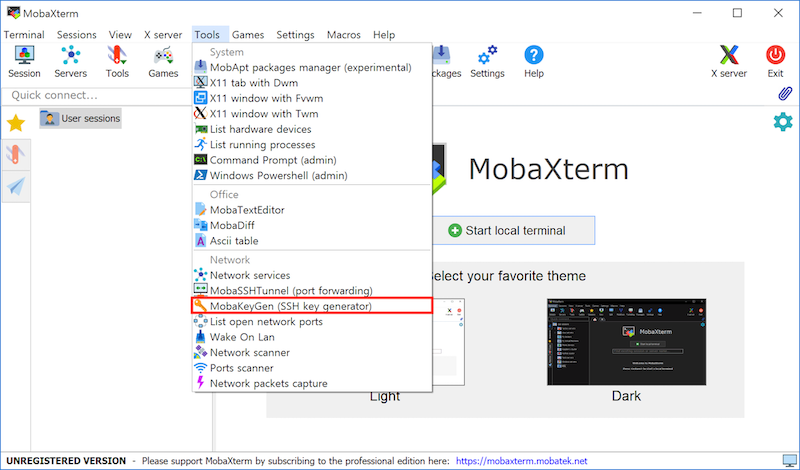
- Select parameters and click
Generate. You can use the below parameters (RSA with 4096bits) or other parameters you want.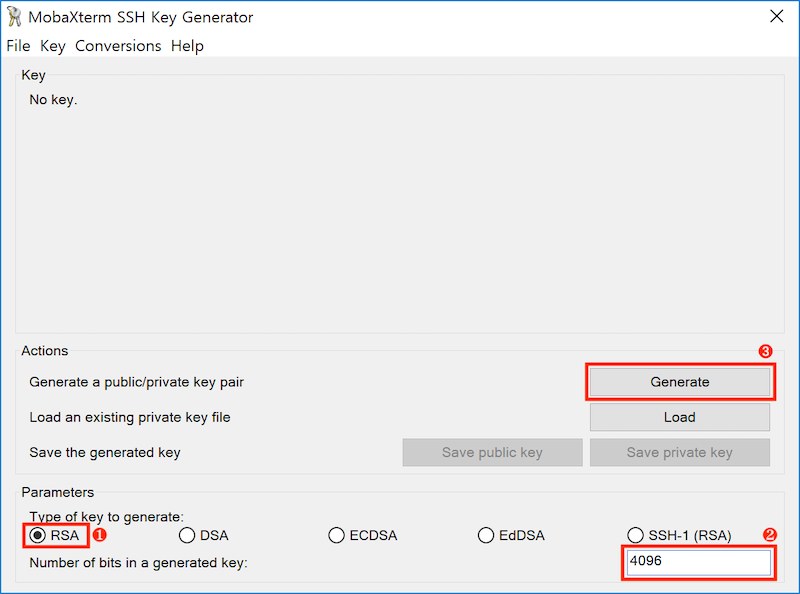
- Move your cursor to generate random numbers. If you don’t, the process will hang.
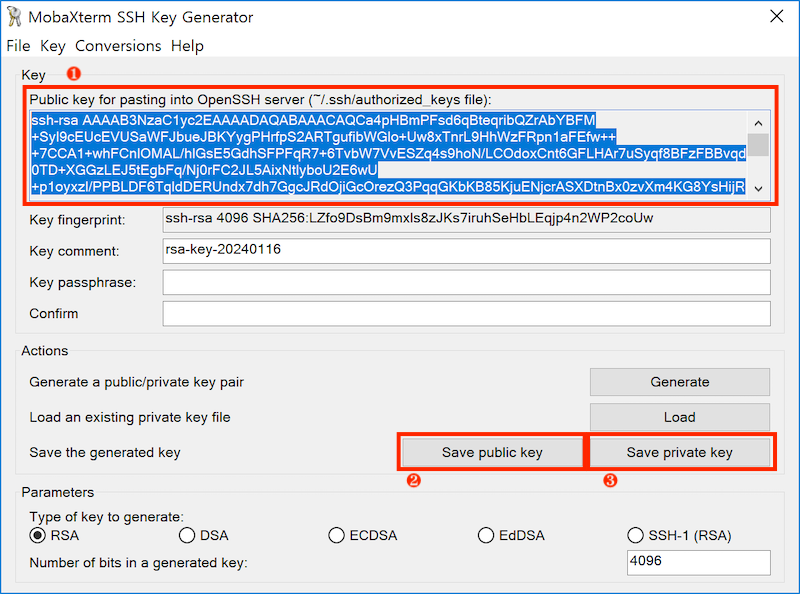
- Copy and paste the generated public key to the account setup page. Save your public and private keys to your preferred location.
+) If you want additional security, typeKey passphrasebefore saving the keys.
- Ubuntu and macOS
- Select
- If you already have an account, click your username at the top right corner and then select
Start/Join Projectand typeutcs356into the ProjectID field.
Once you complete the above steps, the instructor or TA will approve your request to join the project so that you can start an experiment.
Start an Experiment
An experiment in CloudLab means the instantiation of a profile. You can think of a profile as a pre-configured VM image that includes OS and necessary setup. An experiment lasts only for the reserved hours, and all the changes you made on top of the profile will be discarded. Make sure that you use a private git repository to save your code.
- To start a new experiment, go to your CloudLab dashboard and click the
Experimentstab in the upper left corner. Then selectStart Experiment, moving to the profile selection panel.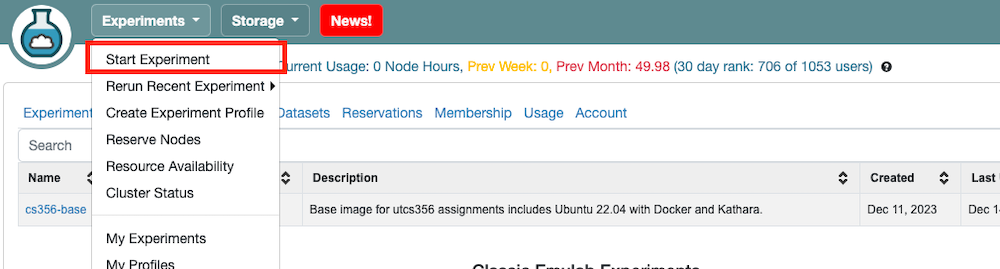
- Click
Change Profile.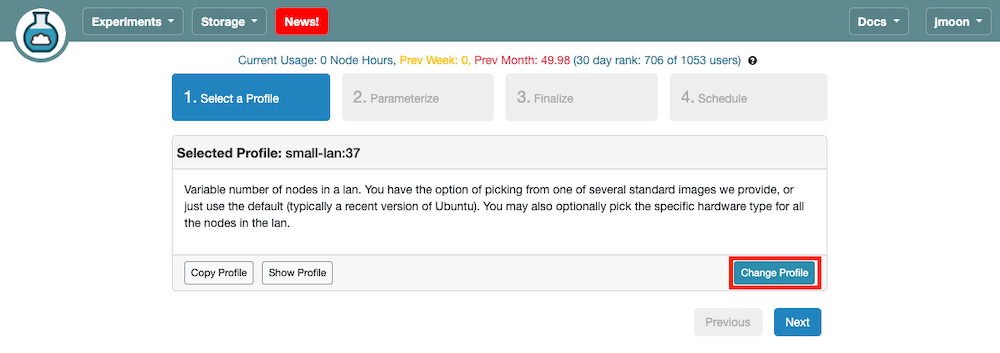
- Select a profile from the list. Choose the
cs356-baseprofile in theutcs356project. With this profile, you can launch one machine with the Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS image with Docker and Kathara additionally installed.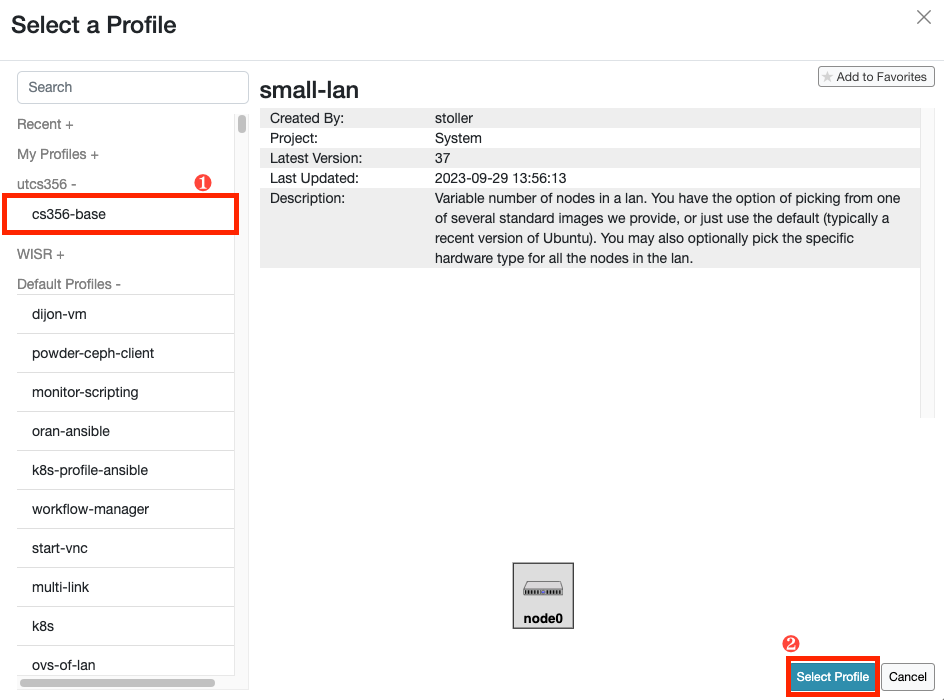
- Click
Nextto move to the next panel (Parameterize).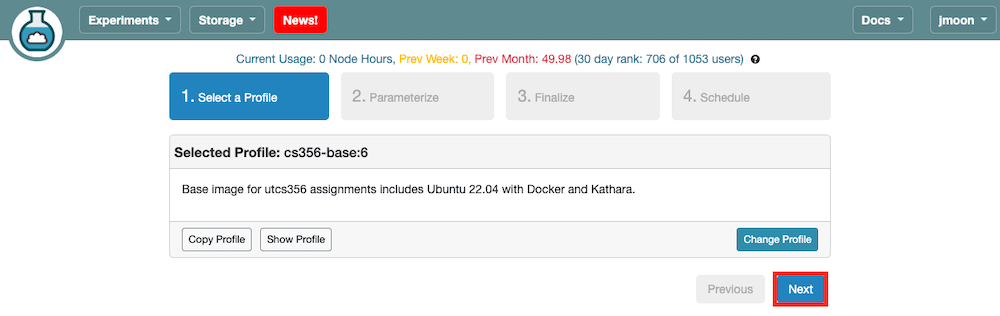
- Click
Nextto move to the next panel (Finalize). You don’t need to parameterize an experiment unless explicitly mentioned.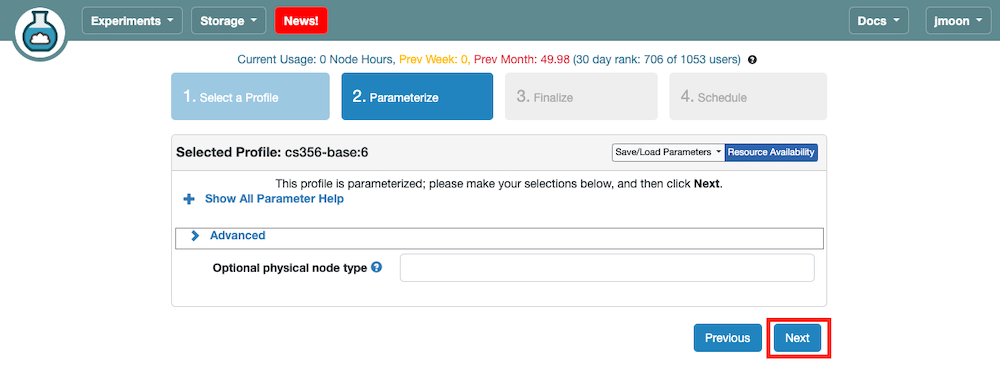
- Here, you should name your experiment with
CSLogin1-CSLogin2(CSLogin1is the cs username of Member 1), selectutcs356asProject, and your assignment group asGroup(You will be invited. If you’re not yet invited,Groupmight not appear. You’re ok to proceed without selectingGroupfor this assignment). You need to specify from which cluster you want to start your experiment. Please select the Wisconsin cluster. If it fails, then try another cluster. ClickNextto move to the next panel (Schedule).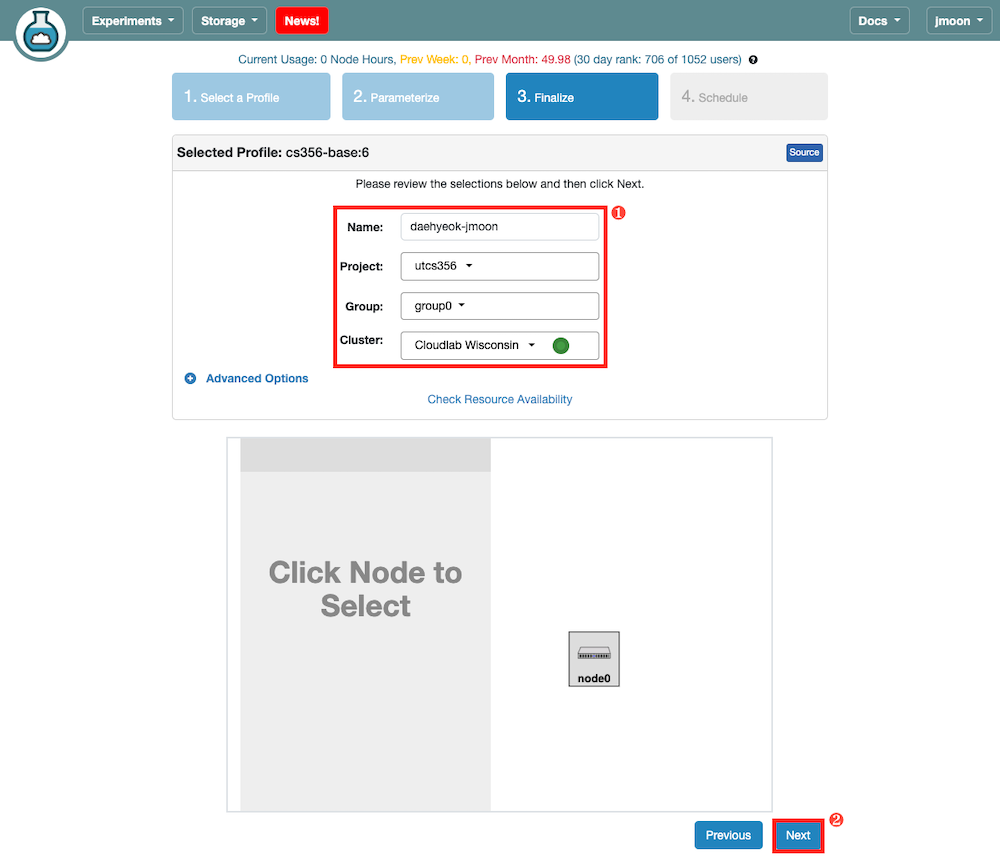
- Enter the desired experiment duration and the time/date when you want to start the experiment. If you want to start your experiment as soon as possible, skip the
Start on date/timefield. Once your experiment is ready you will receive a notification email.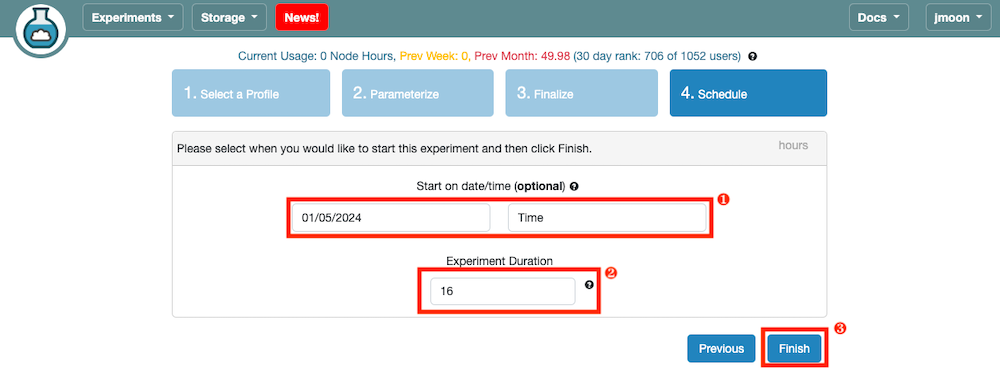
-
You can navigate to your CloudLab user dashboard to see your list of active experiments. You will move to a webpage describing project details by clicking on the experiment name.
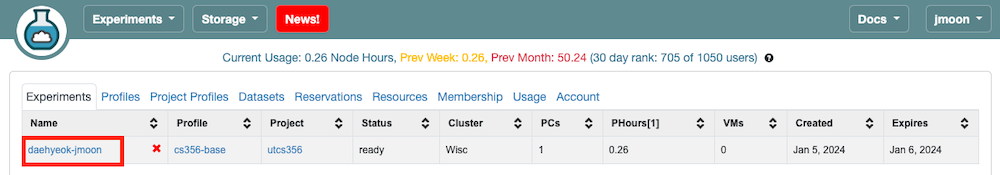 Click the
Click the List Viewon that page, which opens a table where you can obtain the SSH login command (ssh <cloudlab_id>@<cloudlab_host>) to log in to your machine.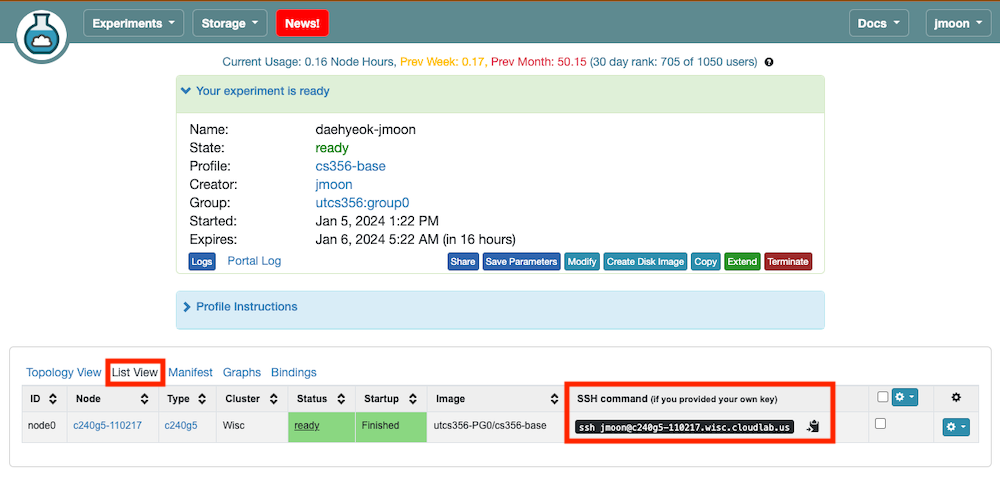
- Try to login to the machine by executing the provided SSH command in your terminal. This step will only work if you have uploaded your SSH public key to your CloudLab account. Add your public key if you did not add it during the registration (here).
- Ubuntu and macOS :
$ ssh <cloudlab_id>@<cloudlab_host> - Windows: On the MobaXterm window,
- Click
Session. - On the SSH tab, type
<cloudlab_host>onRemote host, select theSpecify usernamecheckbox, and type<cloudlab_id>. Select theX11-ForwardingandUse private keycheckboxes. Click the blue file icon and select the private key file you saved in the previous step. Launch an SSH session by clicking onOK.
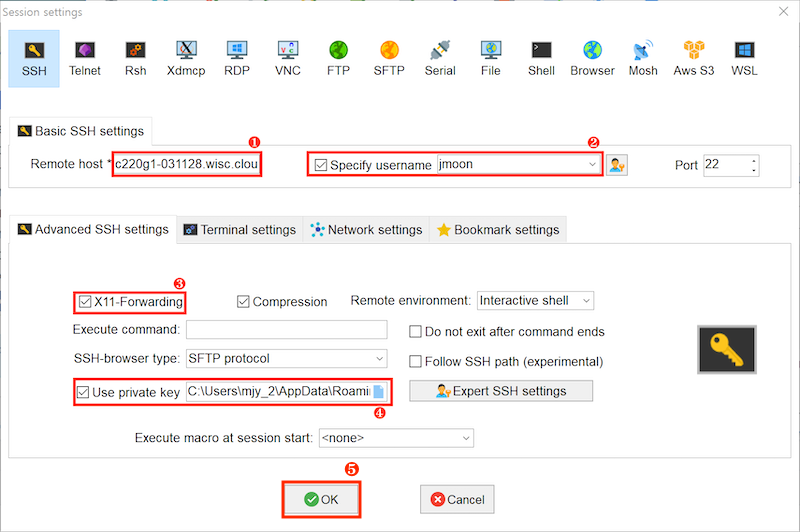
- Click
- Ubuntu and macOS :
If you find yourself stuck on any of the above steps, don’t hesitate to post a question to Ed!
Task
Part 1: Check for the Available Resources
Check for the number of CPU physical cores and logical cores (threads) available (use $ lshw -class cpu or $ lscpu) and memory available (use $ free -h) on the node you reserved.
Report the available resources in your report. If you choose not to use CloudLab and are confident in your ability to debug any issues that come up in your own Linux setup, just write a sentence saying that.
Deliverable
Your report should be a pdf file named assign0_groupX.pdf, where X is your group number. Your report must include your group’s number, members, and their EIDs. Please submit one report per group.
Policies on Using CloudLab Resources
- Please read and follow Cloudlab’s Acceptable Use Policy.
- CloudLab gives users 16 hours to start with, and users can extend it longer. You can manage your time efficiently and only hold onto those nodes when working on the assignment.
- You should use a private git repository to manage your code and terminate the nodes when you are not using them. If you do need to extend the nodes, do not extend them by more than one day. We will terminate any cluster running for more than 48 hours.
- As a member of the
utcs356project, you have permission to create new experiments in the default group in addition to the group you are invited to. Stick to your own group and use naming formats as mentioned. For more information related to this, please refer to https://deanofstudents.utexas.edu/conduct/academicintegrity.php - Each cluster has different hardware. For more information on CloudLab’s hardware, please refer to this.