Invariant local features, instance recognition, bag-of-words models

-
*Object Recognition from Local Scale-Invariant Features, Lowe, ICCV 1999. [pdf] [code] [other implementations of SIFT] [IJCV]
-
*Local Invariant Feature Detectors: A Survey, Tuytelaars and Mikolajczyk. Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Vision, 2008. [pdf] [Oxford code] [Read pp. 178-188, 216-220, 254-255]
-
*Video Google: A Text Retrieval Approach to Object Matching in Videos, Sivic and Zisserman, ICCV 2003. [pdf] [demo]
-
For more background on feature extraction: Szeliski book: Sec 3.2 Linear filtering, 4.1 Points and patches, 4.2 Edges
-
Scalable Recognition with a Vocabulary Tree, D. Nister and H. Stewenius, CVPR 2006. [pdf]
-
SURF: Speeded Up Robust Features, Bay, Ess, Tuytelaars, and Van Gool, CVIU 2008. [pdf] [code]
-
Bundling Features for Large Scale Partial-Duplicate Web Image Search. Z. Wu, Q. Ke, M. Isard, and J. Sun. CVPR 2009. [pdf]
-
Robust Wide Baseline Stereo from Maximally Stable Extremal Regions, J. Matas, O. Chum, U. Martin, and T. Pajdla, BMVC 2002. [pdf]
-
City-Scale Location Recognition, G. Schindler, M. Brown, and R. Szeliski, CVPR 2007. [pdf]
-
Object Retrieval with Large Vocabularies and Fast Spatial Matching. J. Philbin, O. Chum, M. Isard, J. Sivic, and A. Zisserman, CVPR 2007. [pdf]
-
I Know What You Did Last Summer: Object-Level Auto-annotation of Holiday Snaps, S. Gammeter, L. Bossard, T.Quack, L. van Gool, ICCV 2009. [pdf]
-
Total Recall: Automatic Query Expansion with a Generative Feature Model for Object Retrieval. O. Chum et al. CVPR 2007. [pdf]
-
A Performance Evaluation of Local Descriptors. K. Mikolajczyk and C. Schmid. CVPR 2003 [pdf]
- Oxford group interest point software
- Andrea Vedaldi's VLFeat code, including SIFT, MSER, hierarchical k-means.
- INRIA LEAR team's software, including interest points, shape features
- Semantic Robot Vision Challenge links
- CVPR 2009 Workshop on Visual Place Categorization
- Code for downloading Flickr images, by James Hays
- UW Community Photo Collections homepage
- FLANN - Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors. Marius Muja et al.
- Google Goggles
- Kooaba
Global appearance models for category and scene recognition, sliding window detection, detection as a binary decision.

-
*A Discriminatively Trained, Multiscale, Deformable Part Model, by P. Felzenszwalb, D. McAllester and D. Ramanan. CVPR 2008. [pdf] [code]
-
*Beyond Bags of Features: Spatial Pyramid Matching for Recognizing Natural Scene Categories, Lazebnik, Schmid, and Ponce, CVPR 2006. [pdf] [15 scenes dataset] [libpmk] [Matlab]
-
*Rapid Object Detection Using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features, Viola and Jones, CVPR 2001. [pdf] [code]
-
Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection, Dalal and Triggs, CVPR 2005. [pdf] [video] [code] [PASCAL datasets]
-
Modeling the Shape of the Scene: a Holistic Representation of the Spatial Envelope, Oliva and Torralba, IJCV 2001. [pdf] [Gist code]
-
Locality-Constrained Linear Coding for Image Classification. J. Wang, J. Yang, K. Yu, and T. Huang CVPR 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
Visual Categorization with Bags of Keypoints, C. Dance, J. Willamowski, L. Fan, C. Bray, and G. Csurka, ECCV International Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, 2004. [pdf]
-
Pedestrian Detection in Crowded Scenes, Leibe, Seemann, and Schiele, CVPR 2005. [pdf]
-
Pyramids of Histograms of Oriented Gradients (pHOG), Bosch and Zisserman. [code]
-
Eigenfaces for Recognition, Turk and Pentland, 1991. [pdf]
-
Sampling Strategies for Bag-of-Features Image Classification. E. Nowak, F. Jurie, and B. Triggs. ECCV 2006. [pdf]
-
Beyond Sliding Windows: Object Localization by Efficient Subwindow Search. C. Lampert, M. Blaschko, and T. Hofmann. CVPR 2008. [pdf] [code]
-
A Trainable System for Object Detection, C. Papageorgiou and T. Poggio, IJCV 2000. [pdf]
-
Object Recognition with Features Inspired by Visual Cortex. T. Serre, L. Wolf and T. Poggio. CVPR 2005. [pdf]
- LIBPMK feature extraction code, includes dense sampling
- LIBSVM library for support vector machines
- PASCAL
VOC
Visual
Object
Classes Challenge
Segmentation, grouping, surface estimation


-
*Constrained Parametric Min-Cuts for Automatic Object Segmentation. J. Carreira and C. Sminchisescu. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
*Geometric Context from a Single Image, by D. Hoiem, A. Efros, and M. Hebert, ICCV 2005. [pdf] [web] [code]
-
*Contour Detection and Hierarchical Image Segmentation. P. Arbelaez, M. Maire, C. Fowlkes, and J. Malik. PAMI 2011. [pdf] [data and code]
-
From Contours to Regions: An Empirical Evaluation. P. Arbelaez, M. Maire, C. Fowlkes, and J. Malik. CVPR 2009. [pdf] [code]
-
Boundary-Preserving Dense Local Regions. J. Kim and K. Grauman. CVPR 2011. [pdf] [code]
-
Object Recognition as Ranking Holistic Figure-Ground Hypotheses. F. Li, J. Carreira, and C. Sminchisescu. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Using Multiple Segmentations to Discover Objects and their Extent in Image Collections, B. C. Russell, A. A. Efros, J. Sivic, W. T. Freeman, and A. Zisserman. CVPR 2006. [pdf] [code]
-
Combining Top-down and Bottom-up Segmentation. E. Borenstein, E. Sharon, and S. Ullman. CVPR workshop 2004. [pdf] [data]
-
Efficient Region Search for Object Detection. S. Vijayanarasimhan and K. Grauman. CVPR 2011. [pdf] [code] [data]
-
Extracting Subimages of an Unknown Category from a Set of Images, S. Todorovic and N. Ahuja, CVPR 2006. [pdf]
-
Learning Mid-level Features for Recognition. Y.-L. Boureau, F. Bach, Y. LeCun, and J. Ponce. CVPR, 2010.
-
Class-Specific, Top-Down Segmentation, E. Borenstein and S. Ullman, ECCV 2002. [pdf]
-
Object Recognition by Integrating Multiple Image Segmentations, C. Pantofaru, C. Schmid, and M. Hebert, ECCV 2008 [pdf]
-
Image Parsing: Unifying Segmentation, Detection, and Recognition. Tu, Z., Chen, Z., Yuille, A.L., Zhu, S.C. ICCV 2003 [pdf]
-
GrabCut -Interactive Foreground Extraction using Iterated Graph Cuts, by C. Rother, V. Kolmogorov, A. Blake, SIGGRAPH 2004. [pdf] [project page]
-
Recognition Using Regions. C. Gu, J. Lim, P. Arbelaez, J. Malik, CVPR 2009. [pdf] [code]
-
Robust Higher Order Potentials for Enforcing Label Consistency, P. Kohli, L. Ladicky, and P. Torr. CVPR 2008.
-
Co-segmentation of Image Pairs by Histogram Matching --Incorporating a Global Constraint into MRFs, C. Rother, V. Kolmogorov, T. Minka, and A. Blake. CVPR 2006. [pdf]
-
Collect-Cut: Segmentation with Top-Down Cues Discovered in Multi-Object Images. Y. J. Lee and K. Grauman. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [data]
-
An Efficient Algorithm for Co-segmentation, D. Hochbaum, V. Singh, ICCV 2009. [pdf]
-
Normalized Cuts and Image Segmentation, J. Shi and J. Malik. PAMI 2000. [pdf] [code]
- Greg Mori's superpixel code
- Berkeley Segmentation Dataset and code
- Pedro Felzenszwalb's graph-based segmentation code
- Michael Maire's segmentation code and paper
- Mean-shift: a Robust Approach Towards Feature Space Analysis [pdf] [code, Matlab interface by Shai Bagon]
- David Blei's Topic modeling code
Expts: Brian, Cho-Jui
Multi-object scenes, inter-object relationships, understanding scenes' spatial layout, 3d context
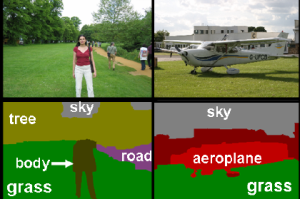
-
*Estimating Spatial Layout of Rooms using Volumetric Reasoning about Objects and Surfaces. D. Lee, A. Gupta, M. Hebert, and T. Kanade. NIPS 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
*Using the Forest to See the Trees: Exploiting Context for Visual Object Detection and Localization. Torralba, Murphy, and Freeman. CACM 2009. [pdf] [related code]
-
Contextual Priming for Object Detection, A. Torralba. IJCV 2003. [pdf] [web] [code]
-
TextonBoost: Joint Appearance, Shape and Context Modeling for Multi-Class Object Recognition and Segmentation. J. Shotton, J. Winn, C. Rother, A. Criminisi. ECCV 2006. [pdf] [web] [data] [code]
-
Recognition Using Visual Phrases. M. Sadeghi and A. Farhadi. CVPR 2011. [pdf]
-
Thinking Inside the Box: Using Appearance Models and Context Based on Room Geometry. V. Hedau, D. Hoiem, and D. Forsyth. ECCV 2010 [pdf] [code and data]
-
Blocks World Revisited: Image Understanding Using Qualitative Geometry and Mechanics, A. Gupta, A. Efros, and M. Hebert. ECCV 2010. [pdf]
-
Object-Graphs for Context-Aware Category Discovery. Y. J. Lee and K. Grauman. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
Geometric Reasoning for Single Image Structure Recovery. D. Lee, M. Hebert, and T. Kanade. CVPR 2009. [pdf] [web] [code]
-
Putting Objects in Perspective, by D. Hoiem, A. Efros, and M. Hebert, CVPR 2006. [pdf] [web]
-
Discriminative Models for Multi-Class Object Layout, C. Desai, D. Ramanan, C. Fowlkes. ICCV 2009. [pdf] [slides] [SVM struct code] [data]
-
Closing the Loop in Scene Interpretation. D. Hoiem, A. Efros, and M. Hebert. CVPR 2008. [pdf]
-
Decomposing a Scene into Geometric and Semantically Consistent Regions, S. Gould, R. Fulton, and D. Koller, ICCV 2009. [pdf] [slides]
-
Learning Spatial Context: Using Stuff to Find Things, by G. Heitz and D. Koller, ECCV 2008. [pdf] [code]
-
An Empirical Study of Context in Object Detection, S. Divvala, D. Hoiem, J. Hays, A. Efros, M. Hebert, CVPR 2009. [pdf] [web]
-
Object Categorization using Co-Occurrence, Location and Appearance, by C. Galleguillos, A. Rabinovich and S. Belongie, CVPR 2008.[ pdf]
-
Context Based Object Categorization: A Critical Survey. C. Galleguillos and S. Belongie. [pdf]
-
What, Where and Who? Classifying Events by Scene and Object Recognition, L.-J. Li and L. Fei-Fei, ICCV 2007. [pdf]
-
Towards Total Scene Understanding: Classification, Annotation and Segmentation in an Unsupervised Framework, L-J. Li, R. Socher, L. Fei-Fei, CVPR 2009. [pdf]
- Labelme Database
- Scene Understanding Symposium
Expts: Saurajit
Among all items in the scene, which deserve attention (first)?
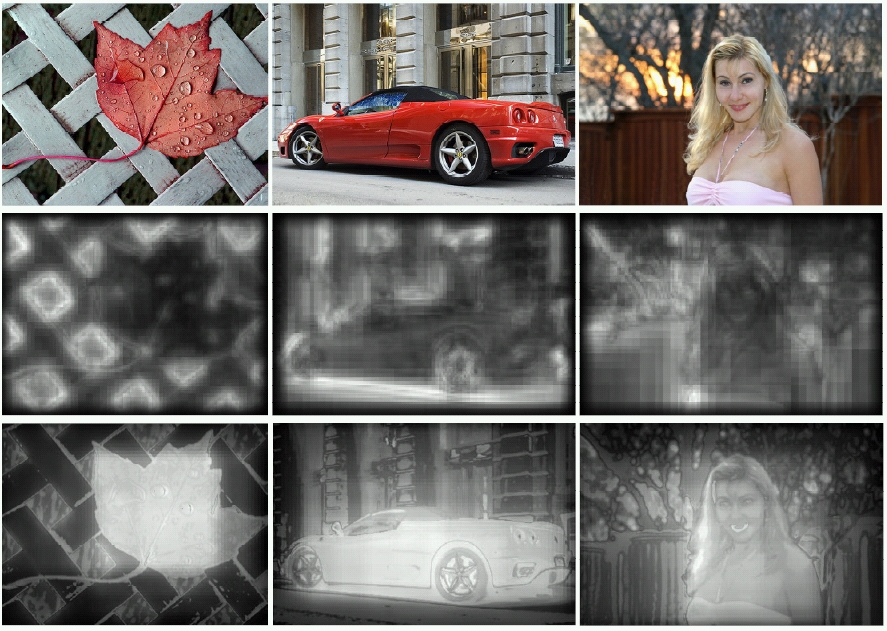

-
*A Model of Saliency-based Visual Attention for Rapid Scene Analysis. L. Itti, C. Koch, and E. Niebur. PAMI 1998 [pdf]
-
*Learning to Detect a Salient Object. T. Liu et al. CVPR 2007. [pdf] [results] [data] [code by Vicente Ordonez]
-
*Figure-Ground Segmentation Improves Handled Object Recognition in Egocentric Video. X. Ren and C. Gu. CVPR 2010 [pdf] [videos] [data]
-
*What Do We Perceive in a Glance of a Real-World Scene? L. Fei-Fei, A. Iyer, C. Koch, and P. Perona. Journal of Vision, 2007. [pdf]
-
Interesting Objects are Visually Salient. L. Elazary and L. Itti. Journal of Vision, 8(3):1–15, 2008. [pdf]
-
Accounting for the Relative Importance of Objects in Image Retrieval. S. J. Hwang and K. Grauman. BMVC 2010. [pdf] [web] [data]
-
Some Objects are More Equal Than Others: Measuring and Predicting Importance, M. Spain and P. Perona. ECCV 2008. [pdf]
- What
Makes an Image Memorable? P. Isola et al. CVPR
2011. [pdf]
-
The Discriminant Center-Surround Hypothesis for Bottom-Up Saliency. D. Gao, V.Mahadevan, and N. Vasconcelos. NIPS, 2007. [pdf]
-
Category-Independent Object Proposals. I. Endres and D. Hoiem. ECCV 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
What is an Object? B. Alexe, T. Deselaers, and V. Ferrari. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
A Principled Approach to Detecting Surprising Events in Video. L. Itti and P. Baldi. CVPR 2005 [pdf]
-
Optimal Scanning for Faster Object Detection, N. Butko, J. Movellan. CVPR 2009. [pdf]
-
What Attributes Guide the Deployment of Visual Attention and How Do They Do It? J. Wolfe and T. Horowitz. Neuroscience, 5:495–501, 2004. [pdf]
-
Visual Correlates of Fixation Selection: Effects of Scale and Time. B. Tatler, R. Baddeley, and I. Gilchrist. Vision Research, 45:643, 2005. [pdf]
-
Objects Predict Fixations Better than Early Saliency. W. Einhauser, M. Spain, and P. Perona. Journal of Vision, 8(14):1–26, 2008. [pdf]
-
Reading Between the Lines: Object Localization Using Implicit Cues from Image Tags. S. J. Hwang and K. Grauman. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [data]
-
Peripheral-Foveal Vision for Real-time Object Recognition and Tracking in Video. S. Gould, J. Arfvidsson, A. Kaehler, B. Sapp, M. Messner, G. Bradski, P. Baumstrack,S. Chung, A. Ng. IJCAI 2007. [pdf]
-
Peekaboom: A Game for Locating Objects in Images, by L. von Ahn, R. Liu and M. Blum, CHI 2006. [pdf] [web]
-
Determining Patch Saliency Using Low-Level Context, D. Parikh, L. Zitnick, and T. Chen. ECCV 2008. [pdf]
-
Visual Recognition and Detection Under Bounded Computational Resources, S. Vijayanarasimhan and A. Kapoor. CVPR 2010.
-
Key-Segments for Video Object Segmentation. Y. J. Lee, J. Kim, and K. Grauman. ICCV 2011 [pdf]
-
Contextual Guidance of Eye Movements and Attention in Real-World Scenes: The Role of Global Features on Object Search. A. Torralba, A. Oliva, M. Castelhano, J. Henderson. [pdf] [web]
-
The Role of Top-down and Bottom-up Processes in Guiding Eye Movements during Visual Search, G. Zelinsky, W. Zhang, B. Yu, X. Chen, D. Samaras, NIPS 2005. [pdf]
Expts: Larry
Visual properties, learning from natural language descriptions, intermediate representations

-
*Attribute and Simile Classifiers for Face Verification, N. Kumar, A. Berg, P. Belhumeur, S. Nayar. ICCV 2009. [pdf] [web] [lfw data] [pubfig data]
-
Relative Attributes. D. Parikh and K. Grauman. ICCV 2011. [pdf] [data]
-
A Discriminative Latent Model of Object Classes and Attributes. Y. Wang and G. Mori. ECCV, 2010. [pdf]
-
Learning Visual Attributes, V. Ferrari and A. Zisserman, NIPS 2007. [pdf]
-
Learning Models for Object Recognition from Natural Language Descriptions, J. Wang, K. Markert, and M. Everingham, BMVC 2009.[pdf]
-
FaceTracer: A Search Engine for Large Collections of Images with Faces. N. Kumar, P. Belhumeur, and S. Nayar. ECCV 2008. [pdf]
-
Attribute-Centric Recognition for Cross-Category Generalization. A. Farhadi, I. Endres, D. Hoiem. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Automatic Attribute Discovery and Characterization from Noisy Web Data. T. Berg et al. ECCV 2010. [pdf] [data]
-
Attributes-Based People Search in Surveillance Environments. D. Vaquero, R. Feris, D. Tran, L. Brown, A. Hampapur, and M. Turk. WACV 2009. [pdf] [project page]
-
Image Region Entropy: A Measure of "Visualness" of Web Images Associated with One Concept. K. Yanai and K. Barnard. ACM MM 2005. [pdf]
-
What Helps Where And Why? Semantic Relatedness for Knowledge Transfer. M. Rohrbach, M. Stark, G. Szarvas, I. Gurevych and B. Schiele. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Recognizing Human Actions by Attributes. J. Liu, B. Kuipers, S. Savarese, CVPR 2011. [pdf]
-
Interactively Building a Discriminative Vocabulary of Nameable Attributes. D. Parikh and K. Grauman. CVPR 2011. [pdf] [web]
Expts: Qiming, Harsh
Discovering the correspondence between words and other language constructs and images, generating descriptions

-
*Baby Talk: Understanding and Generating Image Descriptions. Kulkarni et al. CVPR 2011. [pdf]
-
*Beyond Nouns: Exploiting Prepositions and Comparative Adjectives for Learning Visual Classifiers, A. Gupta and L. Davis, ECCV 2008. [pdf]
-
*Learning Sign Language by Watching TV (using weakly aligned subtitles), P. Buehler, M. Everingham, and A. Zisserman. CVPR 2009. [pdf] [data] [web]
-
Object Recognition as Machine Translation: Learning a Lexicon for a Fixed Image Vocabulary, P. Duygulu, K. Barnard, N. de Freitas, D. Forsyth. ECCV 2002. [pdf] [data]
-
The Mathematics of Statistical Machine Translation: Parameter Estimation. P. Brown, S. Della Pietro, V. Della Pietra, R. Mercer. Association for Computational Linguistics, 1993. [pdf] (background for Duygulu et al paper)
- How Many Words is a Picture Worth?
Automatic Caption Generation for News Images. Y.
Feng and M. Lapata. ACL 2010. [pdf]
-
Matching words and pictures. K. Barnard, P. Duygulu, N. de Freitas, D. Forsyth, D. Blei, and M. Jordan. JMLR, 3:1107–1135, 2003. [pdf]
-
Who's Doing What: Joint Modeling of Names and Verbs for Simultaneous Face and Pose Annotation. L. Jie, B. Caputo, and V. Ferrari. NIPS 2009. [pdf]
-
Watch, Listen & Learn: Co-training on Captioned Images and Videos. S. Gupta, J. Kim, K. Grauman, and R. Mooney. ECML 2008. [pdf]
- Systematic Evaluation of Machine Translation Methods for Image and Video Annotation, P. Virga, P. Duygulu, CIVR 2005. [pdf]
- Localizing Objects and Actions in Videos Using Accompanying Text. Johns Hopkins University Summer Workshop Report. J. Neumann et al. 2010. [pdf] [web]
- Subrip for subtitle extraction
- Reuters captioned photos
- Sonal Gupta's data for commentary+video
Expts: Jae, Naga
Human-in-the-loop learning, active annotation collection, crowdsourcing


-
*Large-Scale Live Active Learning: Training Object Detectors with Crawled Data and Crowds. S. Vijayanarasimhan and K. Grauman. CVPR 2011. [pdf]
-
*Visual Recognition with Humans in the Loop. Branson S., Wah C., Babenko B., Schroff F., Welinder P., Perona P., Belongie S. ECCV 2010. [pdf] [Caltech/UCSD Visipedia project] [data]
-
*The Multidimensional Wisdom of Crowds. Welinder P., Branson S., Belongie S., Perona, P. NIPS 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
*What’s It Going to Cost You? : Predicting Effort vs. Informativeness for Multi-Label Image Annotations. S. Vijayanarasimhan and K. Grauman. CVPR 2009 [pdf] [data] [code]
-
iCoseg: Interactive Co-segmentation with Intelligent Scribble Guidance, D. Batra, A. Kowdle, D. Parikh, J. Luo and T. Chen. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [web]
-
Labeling Images with a Computer Game. L. von Ahn and L. Dabbish. CHI, 2004.
- Who's Vote Should Count More: Optimal
Integration fo Labels from Labelers of Unknown
Expertise. J. Whitehill et al. NIPS
2009. [pdf]
-
Utility Data Annotation with Amazon Mechanical Turk. A. Sorokin and D. Forsyth. Wkshp on Internet Vision, 2008.
-
Far-Sighted Active Learning on a Budget for Image and Video Recognition. S. Vijayanarasimhan, P. Jain, and K. Grauman. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [code]
-
Multiclass Recognition and Part Localization with Humans in the Loop. C. Wah et al. ICCV 2011. [pdf]
-
Multi-Level Active Prediction of Useful Image Annotations for Recognition. S. Vijayanarasimhan and K. Grauman. NIPS 2008. [pdf]
-
Active Learning from Crowds. Y. Yan, R. Rosales, G. Fung, J. Dy. ICML 2011. [pdf]
- Proactive Learning:
Cost-Sensitive Active Learning with Multiple
Imperfect Oracles. P. Donmez and J.
Carbonell. CIKM 2008. [pdf]
-
Inactive Learning? Difficulties Employing Active Learning in Practice. J. Attenberg and F. Provost. SIGKDD 2011. [pdf]
-
Annotator Rationales for Visual Recognition. J. Donahue and K. Grauman. ICCV 2011. [pdf]
-
Interactively Building a Discriminative Vocabulary of Nameable Attributes. D. Parikh and K. Grauman. CVPR 2011. [pdf] [web]
-
Actively Selecting Annotations Among Objects and Attributes. A. Kovashka, S. Vijayanarasimhan, and K. Grauman. ICCV 2011 [pdf]
- Supervised
Learning from Multiple Experts: Whom to Trust When
Everyone Lies a Bit. V. Raykar et al.
ICML 2009. [pdf]
-
Multi-class Active Learning for Image Classification. A. J. Joshi, F. Porikli, and N. Papanikolopoulos. CVPR 2009. [pdf]
-
GrabCut -Interactive Foreground Extraction using Iterated Graph Cuts, by C. Rother, V. Kolmogorov, A. Blake, SIGGRAPH 2004. [pdf] [project page]
-
Active Learning for Piecewise Planar 3D Reconstruction. A. Kowdle, Y.-J. Chang, A. Gallagher and T. Chen. CVPR 2011 [pdf] [web]
- Amazon Mechanical Turk
- Using Mechanical Turk with LabelMe
Expts: Yunsik
Finding people and their poses, automatic face tagging

-
*Poselets: Body Part Detectors Trained Using 3D Human Pose Annotations, L. Bourdev and J. Malik. ICCV 2009 [pdf] [code]
-
*Understanding Images of Groups of People, A. Gallagher and T. Chen, CVPR 2009. [pdf] [web] [data]
-
*Real-Time Human Pose Recognition in Parts from a Single Depth Image. J. Shotton et al. CVPR 2011. [pdf] [video]
-
*"'Who are you?' - Learning Person Specific Classifiers from Video, J. Sivic, M. Everingham, and A. Zisserman, CVPR 2009. [pdf] [data] [KLT tracking code]
-
Contextual Identity Recognition in Personal Photo Albums. D. Anguelov, K.-C. Lee, S. Burak, Gokturk, and B. Sumengen. CVPR 2007. [pdf]
-
Fast Pose Estimation with Parameter Sensitive Hashing. G. Shakhnarovich, P. Viola, T. Darrell, ICCV 2003.[pdf]
-
Finding and Tracking People From the Bottom Up. D. Ramanan, D. A. Forsyth. CVPR 2003. [pdf]
-
Where’s Waldo: Matching People in Images of Crowds. R. Garg, D. Ramanan, S. Seitz, N. Snavely. CVPR 2011. [pdf]
-
Autotagging Facebook: Social Network Context Improves Photo Annotation, by Z. Stone, T. Zickler, and T. Darrell. CVPR Internet Vision Workshop 2008. [pdf]
-
Efficient Propagation for Face Annotation in Family Albums. L. Zhang, Y. Hu, M. Li, and H. Zhang. MM 2004. [pdf]
-
Progressive Search Space Reduction for Human Pose Estimation. Ferrari, V., Marin-Jimenez, M. and Zisserman, A. CVPR 2008. [pdf] [web] [code]
- Leveraging
Archival Video for Building Face Datasets, by D.
Ramanan, S. Baker, and S. Kakade. ICCV
2007. [pdf]
-
Names and Faces in the News, by T. Berg, A. Berg, J. Edwards, M. Maire, R. White, Y. Teh, E. Learned-Miller and D. Forsyth, CVPR 2004. [pdf] [web]
-
Face Discovery with Social Context. Y. J. Lee and K. Grauman. BMVC 2011. [pdf]
-
“Hello! My name is... Buffy” – Automatic Naming of Characters in TV Video, by M. Everingham, J. Sivic and A. Zisserman, BMVC 2006. [pdf] [web] [data]
-
Modeling Mutual Context of Object and Human Pose in Human-Object Interaction Activities. Yao, B., Fei-Fei, L. CVPR 2010.
-
A Face Annotation Framework with Partial Clustering and Interactive Labeling. R. X. Y. Tian,W. Liu, F.Wen, and X. Tang. CVPR 2007. [pdf] [web]
-
From 3D Scene Geometry to Human Workspace. A. Gupta et al. CVPR 2011. [pdf] [web]
-
Pictorial Structures Revisited: People Detection and Articulated Pose Estimation. M. Andriluka et al. CVPR 2009. [pdf] [code]
- Face detection code in OpenCV
- Gallagher's Person Dataset
- Face data from Buffy episode, from Oxford Visual Geometry Group
- CALVIN
upper-body detector code
Expts: Nishant, Jung
Recognizing and localizing human actions in video

-
*Actions in Context, M. Marszalek, I. Laptev, C. Schmid. CVPR 2009. [pdf] [web] [data]
-
*A Hough Transform-Based Voting Framework for Action Recognition. A. Yao, J. Gall, L. Van Gool. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [code/data]
-
*Beyond Actions: Discriminative Models for Contextual Group Activities. T. Lian, Y. Wang, W. Yang, and G. Mori. NIPS 2010. [pdf] [data]
-
Objects in Action: An Approach for Combining Action Understanding and Object Perception. A. Gupta and L. Davis. CVPR, 2007. [pdf] [data]
-
Learning Realistic Human Actions from Movies. I. Laptev, M. Marszałek, C. Schmid and B. Rozenfeld. CVPR 2008. [pdf] [data]
-
Understanding Egocentric Activities. A. Fathi, A. Farhadi, J. Rehg. ICCV 2011. [pdf]
-
Exploiting Human Actions and Object Context for Recognition Tasks. D. Moore, I. Essa, and M. Hayes. ICCV 1999. [pdf]
-
A Scalable Approach to Activity Recognition Based on Object Use. J. Wu, A. Osuntogun, T. Choudhury, M. Philipose, and J. Rehg. ICCV 2007. [pdf]
-
Recognizing Actions at a Distance. A. Efros, G. Mori, J. Malik. ICCV 2003. [pdf] [web]
-
Activity Recognition from First Person Sensing. E. Taralova, F. De la Torre, M. Hebert CVPR 2009 Workshop on Egocentric Vision [pdf]
-
Action Recognition from a Distributed Representation of Pose and Appearance, S. Maji, L. Bourdev, J. Malik, CVPR 2011. [pdf] [code]
-
Learning a Hierarchy of Discriminative Space-Time Neighborhood Features for Human Action Recognition. A. Kovashka and K. Grauman. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Temporal Causality for the Analysis of Visual Events. K. Prabhakar, S. Oh, P. Wang, G. Abowd, and J. Rehg. CVPR 2010. [pdf] [Georgia Tech Computational Behavior Science project]
-
Modeling Activity Global Temporal Dependencies using Time Delayed Probabilistic Graphical Model. Loy, Xiang & Gong ICCV 2009. [pdf]
-
What's Going on?: Discovering Spatio-Temporal Dependencies in Dynamic Scenes. D. Kuettel et al. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Learning Actions From the Web. N. Ikizler-Cinbis, R. Gokberk Cinbis, S. Sclaroff. ICCV 2009. [pdf]
- Content-based Retrieval of Functional Objects in Video Using Scene Context. S. Oh, A. Hoogs, M. Turek, and R. Collins. ECCV 2010. [pdf]
- Ivan Laptev's Space-Time Interest Points code
- Hollywood activity dataset
- UCF activity datasets
- PASCAL VOC action recognition taster challenge
- Greg Mori and Ivan Laptev's tutorial on action recognition at ECCV 2010
- TRECVID video retrieval challenge
- UMich
Collective
Activity dataset
Expts: Lu Xia
Sharing features between classes, transfer, taxonomy, learning from few examples, exploiting class relationships
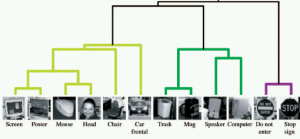
-
*Sharing Visual Features for Multiclass and Multiview Object Detection, A. Torralba, K. Murphy, W. Freeman, PAMI 2007. [pdf] [code]
-
*What Does Classifying More than 10,000 Image Categories Tell Us? J. Deng, A. Berg, K. Li and L. Fei-Fei. ECCV 2010. [pdf]
-
*Discriminative Learning of Relaxed Hierarchy for Large-scale Visual Recognition. T. Gao and Daphne Koller. ICCV 2011. [pdf] [code]
-
Comparative Object Similarity for Improved Recognition with Few or Zero Examples. G. Wang, D. Forsyth, and D. Hoeim. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Learning and Using Taxonomies for Fast Visual Categorization, G. Griffin and P. Perona, CVPR 2008. [pdf] [data]
-
Cross-Generalization: Learning Novel Classes from a Single Example by Feature Replacement. CVPR 2005. [pdf]
-
80 Million Tiny Images: A Large Dataset for Non-Parametric Object and Scene Recognition, by A. Torralba, R. Fergus, and W. Freeman. PAMI 2008. [pdf] [web]
-
Constructing Category Hierarchies for Visual Recognition, M. Marszalek and C. Schmid. ECCV 2008. [pdf] [web] [Caltech256]
-
Learning Generative Visual Models from Few Training Examples: an Incremental Bayesian Approach Tested on 101 Object Categories. L. Fei-Fei, R. Fergus, and P. Perona. CVPR Workshop on Generative-Model Based Vision. 2004. [pdf] [Caltech101]
-
Towards Scalable Representations of Object Categories: Learning a Hierarchy of Parts. S. Fidler and A. Leonardis. CVPR 2007 [pdf]
-
Exploiting Object Hierarchy: Combining Models from Different Category Levels, A. Zweig and D. Weinshall, ICCV 2007 [pdf]
-
Incremental Learning of Object Detectors Using a Visual Shape Alphabet. Opelt, Pinz, and Zisserman, CVPR 2006. [pdf]
-
Sequential Learning of Reusable Parts for Object Detection. S. Krempp, D. Geman, and Y. Amit. 2002 [pdf]
-
ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database, J. Deng, W. Dong, R. Socher, L.-J. Li, K. Li and L. Fei-Fei, CVPR 2009 [pdf] [data]
-
Semantic Label Sharing for Learning with Many Categories. R. Fergus et al. ECCV 2010. [pdf]
-
Learning a Tree of Metrics with Disjoint Visual Features. S. J. Hwang, K. Grauman, F. Sha. NIPS 2011.
Expts: Lu Pan
Scalable retrieval algorithms for massive databases, mining for themes
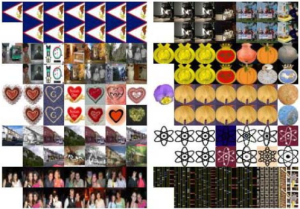
-
*VisualRank: Applying PageRank to Large-Scale Image Search. Y. Jing and S. Baluja. PAMI 2008. [pdf]
-
*Kernelized Locality Sensitive Hashing for Scalable Image Search, by B. Kulis and K. Grauman, ICCV 2009 [pdf] [code]
-
*Video Mining with Frequent Itemset Configurations. T. Quack, V. Ferrari, and L. Van Gool. CIVR 2006. [pdf]
-
Learning Binary Projections for Large-Scale Image Search. K. Grauman and R. Fergus. Chapter (draft) to appear in Registration, Recognition, and Video Analysis, R. Cipolla, S. Battiato, and G. Farinella, Editors. [pdf]
-
World-scale Mining of Objects and Events from Community Photo Collections. T. Quack, B. Leibe, and L. Van Gool. CIVR 2008. [pdf]
-
Interest Seam Image. X. Zhang, G. Hua, L. Zhang, H. Shum. CVPR 2010. [pdf]
-
Detecting Objects in Large Image Collections and Videos by Efficient Subimage Retrieval, C. Lampert, ICCV 2009. [pdf] [code]
-
Geometric Min-Hashing: Finding a (Thick) Needle in a Haystack, O. Chum, M. Perdoch, and J. Matas. CVPR 2009. [pdf]
-
FaceTracer: A Search Engine for Large Collections of Images with Faces. N. Kumar, P. Belhumeur, and S. Nayar. ECCV 2008. [pdf]
-
Efficiently Searching for Similar Images. K. Grauman. Communications of the ACM, 2009. [CACM link]
-
Fast Image Search for Learned Metrics, P. Jain, B. Kulis, and K. Grauman, CVPR 2008. [pdf]
-
Small Codes and Large Image Databases for Recognition, A. Torralba, R. Fergus, and Y. Weiss, CVPR 2008. [pdf]
-
Object Retrieval with Large Vocabularies and Fast Spatial Matching. J. Philbin, O. Chum, M. Isard, J. Sivic, and A. Zisserman, CVPR 2007. [pdf]
- LSH homepage
- Nearest Neighbor Methods in Learning and Vision, Shakhnarovich, Darrell, and Indyk, editors.
Expts: Si Si
Video synopsis, discovering repeated objects, visualization

-
*Webcam Synopsis: Peeking Around the World, by Y. Pritch, A. Rav-Acha, A. Gutman, and S. Peleg, ICCV 2007. [pdf] [web]
-
*Using Multiple Segmentations to Discover Objects and their Extent in Image Collections, B. C. Russell, A. A. Efros, J. Sivic, W. T. Freeman, and A. Zisserman. CVPR 2006. [pdf] [code]
-
*Summarizing Visual Data Using Bi-Directional Similarity. D. Simakov, Y. Caspi, E. Shechtmann, M. Irani. CVPR 2008. [pdf] [video]
-
Fast Unsupervised Ego-Action Learning for First-Person Sports Video. K. Kitani, T. Okabe, Y. Sato, A. Sugimoto. CVPR 2011. [pdf]
-
Scene Summarization for Online Image Collections. I. Simon, N. Snavely, S. Seitz. ICCV 2007. [pdf] [web]
-
VideoCut: Removing Irrelevant Frames by Discovering the Object of Interest. D. Liu, G. Hua, T. Chen. ECCV 2010. [pdf]
-
Video Epitomes. V. Cheung, B. J. Frey, and N. Jojic. CVPR 2005. [pdf] [web] [code]
-
Making a Long Video Short. A. Rav-Acha, Y. Pritch, and S. Peleg. CVPR 2006. [pdf]
-
Structural Epitome: A Way to Summarize One's Visual Experience. N. Jojic, A. Perina, V. Murino. NIPS 2010. [pdf] [data]
-
Video Abstraction: A Systematic Review and Classification. B. Truong and S. Venkatesh. ACM 2007. [pdf]
- Shape Discovery from Unlabeled Image Collections. Y. J. Lee and K. Grauman. CVPR 2009. [pdf]
Expts: Sunil, Chris