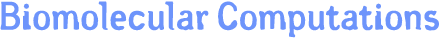| Biography | Research | Publications | Teaching | Group | Projects | Software | Sponsors | Collaborators |
|
|||||
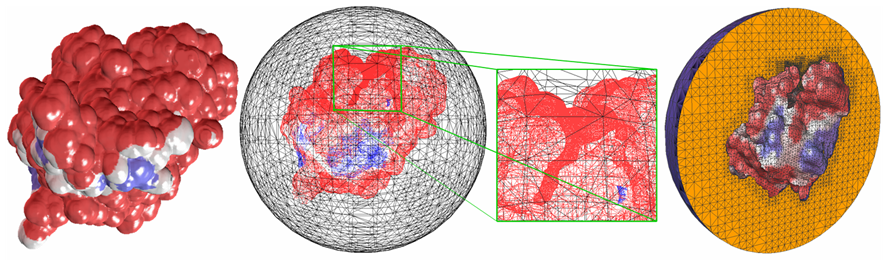
This paper describes an algorithm to extract adaptive and quality 3D meshes directly from volumetric imaging data. The extracted tetrahedral and hexahedral meshes are extensively used in the Finite Element Method (FEM). A top-down octree subdivision coupled with the dual contouring method is used to rapidly extract adaptive 3D finite element meshes with correct topology from volumetric imaging data. The edge contraction and smoothing methods are used to improve the mesh quality. The main contribution is extending the dual contouring method to crack-free interval volume 3D meshing with feature sensitive adaptation. Compared to other tetrahedral extraction methods from imaging data, our method generates adaptive and quality 3D meshes without introducing any hanging nodes. The algorithm has been successfully applied to constructing the geometric model of a biomolecule in finite element calculations.
Result ( Images and Video )
( Each image is linked to a higher resolution image. Please click the title of each model for more detailed description of the corresponding project. )1. Biomolecular Modeling ( Mouse Acetylcholinesterase [mAChE] )
|
2. Biomolecular Modeling ( Hemoglobin )
|
References
Y. Zhang, C. Bajaj, B-S. SohnAdaptive and Quality 3D Meshing from Imaging Data
Proceedings of 8th ACM Symposium on Solid Modeling and Applications.
Pages 286-291. Seattle, WA. June 16-20, 2003.
Y. Song, Y. Zhang, T. Shen, C. Bajaj, J. McCammon, N. Baker
Finite Element Solution of the Steady-state Smolchowski Equation for Rate Constant Calculations
Accepted in Biophysical Journal